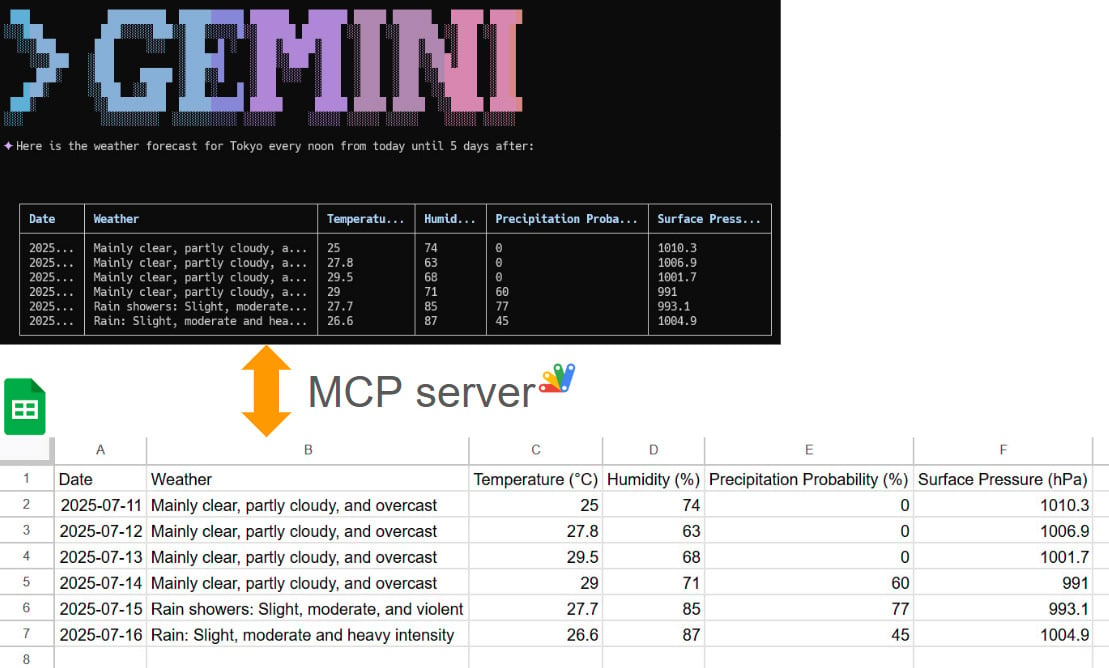
This article explores the integration of the Gemini Command-Line Interface (CLI) with Google Sheets using the Model Context Protocol (MCP). It demonstrates how to leverage the open-source projects MCPApp and ToolsForMCPServer to create a bridge between the Gemini CLI and Google Workspace. This enables users to perform powerful data automation tasks, such as creating, reading, and modifying tables in Google Sheets directly from the command line, using natural language prompts. The article provides practical examples and sample prompts to illustrate the seamless workflow and potential for building sophisticated, AI-powered applications within the Google Cloud ecosystem.
For developers who work in the command line, the introduction of Google’s Gemini Command-Line Interface (CLI) has opened up new ways to interact with AI. The open-source tool allows you to bring the power of Gemini models directly into your terminal, making it a useful companion for coding assistance, content generation, and task automation. While the CLI can interact with your local file system and the internet, its standard capabilities don’t provide a direct path to your personal data within Google Workspace.
But what if you could extend it? What if you could create a secure connection, allowing the Gemini CLI to interact with your own files in Drive, events in Calendar, or emails in Gmail?
Over the past month, Google Workspace Developer Expert Kanshi Tanaike has published an insightful series of blog posts that provides a practical blueprint for achieving just that. In this series, he demonstrates how to use the flexibility of Google Apps Script to create a powerful, personalised bridge between the Gemini CLI and the entire suite of Google Workspace services.
At the centre of Kanshi’s solution is a simple and effective architecture. He shows readers how to build a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server using a Google Apps Script project deployed as a Web App. This server acts as the secure intermediary between the Gemini CLI and your Google account.
The key advantage of this approach lies in its security and simplicity. By using Apps Script, the complex and critical OAuth2 authorisation is handled natively within the Google ecosystem. This means developers can create a robust tool without the overhead of managing credentials or setting up separate cloud infrastructure.
Throughout the series, Kanshi doesn’t just provide the theory; he delivers the tools to make it happen. He has developed and shared two key open-source Apps Script libraries, MCPApp and ToolsForMCPServer, which significantly simplify the process. These libraries provide a ready-to-use framework and a rich set of functions for interacting with Workspace services.
The result is a system capable of executing complex, multi-step automations from a single, natural-language prompt. The examples in his posts speak for themselves:
- Automated Data Entry: Fetching a multi-day weather forecast and populating it directly into a Google Sheet.
- Content Creation: Uploading a local PDF to Drive, generating a summary, creating a new Google Slides presentation from that summary, and emailing it to a colleague.
- Interactive Tasks: Generating a custom survey in Google Forms and sending out the link via Gmail.
This extensibility is what sets the approach apart. While a standard tool like the Gemini App (gemini.google.com) provides a familiar conversational interface, it offers a fixed set of features. This CLI-based method allows developers to keep that same intuitive, conversational style of interaction but makes it completely extensible. With the CLI and a custom MCP server, developers are no longer limited—they can build bespoke tools to solve their specific challenges.
For example, a common request from Workspace users is the ability to generate an entire presentation from source material. Using this framework, a developer could easily build a custom tool to do just that, triggered by a single command.
This series is a great example of the innovation happening within the Google Workspace developer community. While this command-line approach is naturally suited for developers and power users comfortable with scripting, it offers a level of control and automation that is difficult to achieve through graphical interfaces. It provides a clear, powerful, and extensible pattern for anyone in this group looking to explore their own sophisticated AI-powered automations.
We highly recommend diving into the series to see what’s possible. You can start with the most recent post, which links back to the previous articles in the series:
Source: Next-Level Data Automation: Gemini CLI, Google Sheets, and MCP

Member of Google Developers Experts Program for Google Workspace (Google Apps Script) and interested in supporting Google Workspace Devs.